Risk management and internal control systems
KEGOC JSC has successfully implemented and operates a risk management system, which is based on the generally accepted conceptual models of risk management developed by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission — COSO ERM ‘Organizational Risk Management. Integrated Model’ and requirements of Samruk-Kazyna JSC.
The corporate risk management system is a key component of the corporate governance system aimed at the timely identification of risks, their assessment and the development of risk management measures that may adversely affect the achievement of KEGOC JSC strategic and operational objectives.
The purpose of the current CRMS is to ensure continuity and stability of operations by limiting the degree of impact of internal and external negative factors on KEGOC JSC operations.
The main principles of the risk management system are as follows:
- involvement of the Company’s management in risk management;
- continuous improvement of the risk management system;
- continuous training and knowledge sharing in the area of risk management by the Company’s employees;
- openness and honesty in reporting and escalation of risks.
The objectives of the risk management system are as follows:
- development and application of uniform and consistent approaches to identifying, assessing and managing KEGOC JSC risks, simplification of procedures for sharing information on risks vertically (management) and horizontally (exchange of experience);
- prompt response to emerging risk events, tracking changes in the external and internal environment;
- organization of targeted risk management activities to reduce risks to an acceptable level or transfer them to third parties (outsourcing, insurance, hedging) or risk avoidance;
- systematization and further accumulation of information on KEGOC JSC risks, improvement of KEGOC JSC manageability;
- improvement of KEGOC JSC competitiveness and achievement of KEGOC JSC strategic goals by increasing the efficiency of the RMS.
The RMS serves as a tool supporting the management decision-making process and daily operational activities of KEGOC JSC.
The risk management process at KEGOC JSC is permanent, cyclical (continuous), multi-directional and consists of the following components:
- Internal Environment;
- Goal setting;
- Identifying risks;
- Risk assessment;
- Risk Management;
- Controls;
- Information and Communication;
- Monitoring.
KEGOC JSC risk management process
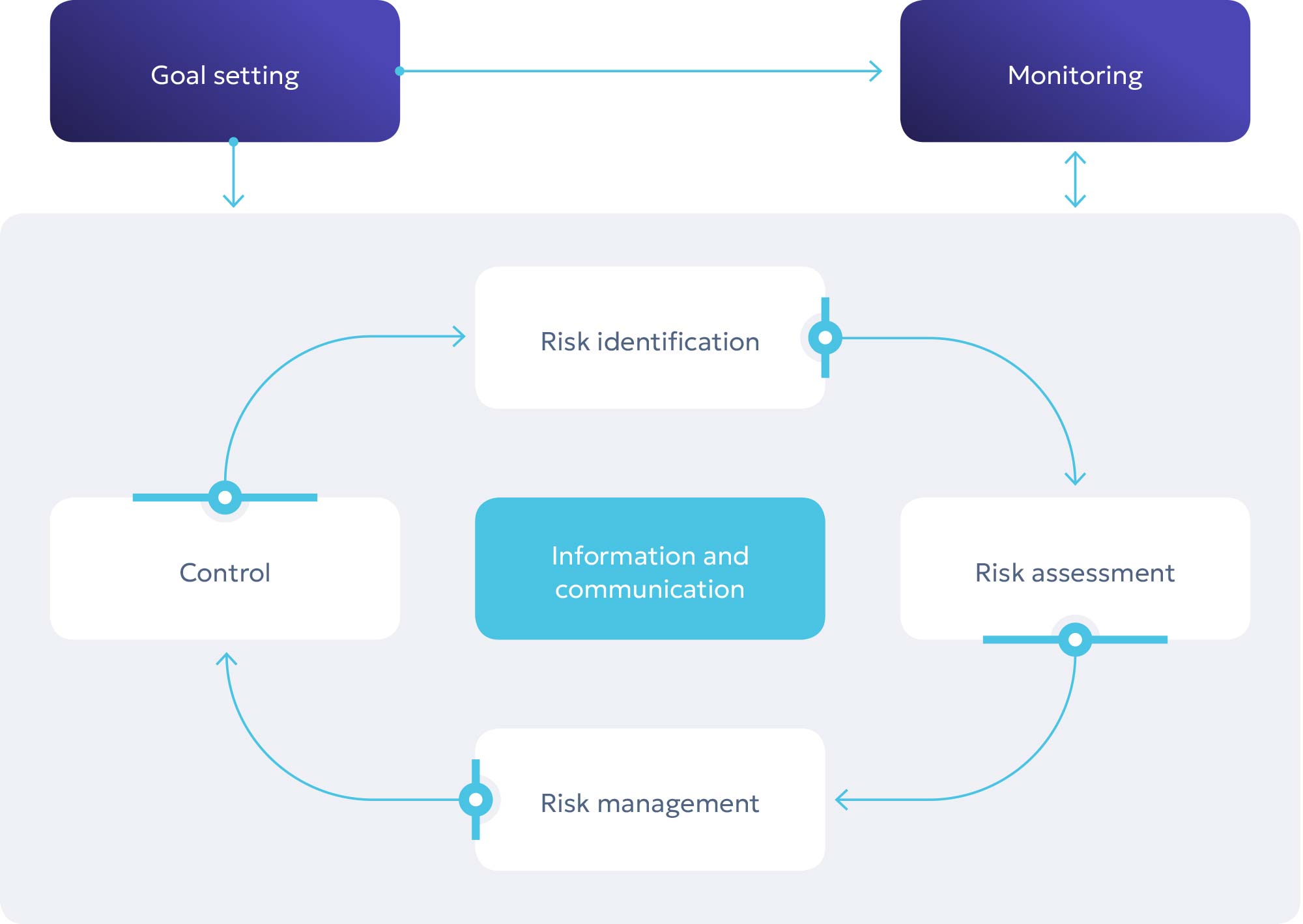
Implementation of the above components of the risk management process contributes to the development of risk management culture (risk culture), which is the basis of risk management. It comprises beliefs, understanding and knowledge in the field of risk management, shared and applied by all officers and employees in the performance of their duties.
Risk culture is part of the corporate culture. The level of risk culture determines how risks are identified, assessed and managed from the development of the Development Plan through to its implementation and performance monitoring.
The risk culture is based on the following principles:
- Tone at the top: Decision-making is based on an optimal balance between long-term value, profitability and the risks associated with both making and not making decisions, and management encourages risk-oriented behavior in subordinates.
- Corporate Governance: KEGOC JSC activities are aimed at creating a control environment that ensures that employees understand that the Policy and all IRDs are binding. All officers and employees of KEGOC JSC clearly recognize their area of responsibility and authority for risk management and internal control. Risk Owners, within the scope of their competence, understand and manage risks and properly communicate risks in accordance with KEGOC JSC INEDs.
- Decision-making: The internal environment is characterized by open communication and transparency of risk information, which facilitates open and constructive discussion of associated risks and potential opportunities between employees and management, allowing for joint effective decision-making in response to external challenges.
- The remuneration system at all levels uses financial and non-financial incentives for management and employees to form the right attitude to risk in the process of making managerial decisions. With a well-developed risk culture, decisions are clearly defined by the Risk Appetite.
- Competence:KEGOC JSC organizational structure is based on the ‘three lines of defense’ model. The Risk Unit effectively fulfils the role of the second line of defense, thereby increasing Management’s confidence in achieving KEGOC JSC objectives.
One of the sources of information on the level of risk culture for the Management Board and the Board of Directors are documents on assessment of RMS efficiency, reports on diagnostics of corporate governance in the Company.
To improve risk culture, the Company provides briefing/seminars for newly hired employees in the area of the Company’s RMS, and the Company’s senior management takes part in specialised risk management seminars and trainings aimed at senior executives.
To control the level of risk culture development in the Company, in 2023, a questionnaire (survey) of employees/testing of knowledge in the field of RMS was conducted to assess the effectiveness of risk management at the workplace. Based on the results of the survey, seminars for employees of structural divisions are planned for 2024. In addition, KEGOC JSC employees were tested on their knowledge of risk management and internal control systems, which was successfully passed by all tested employees.
Organizational structure of the RMS
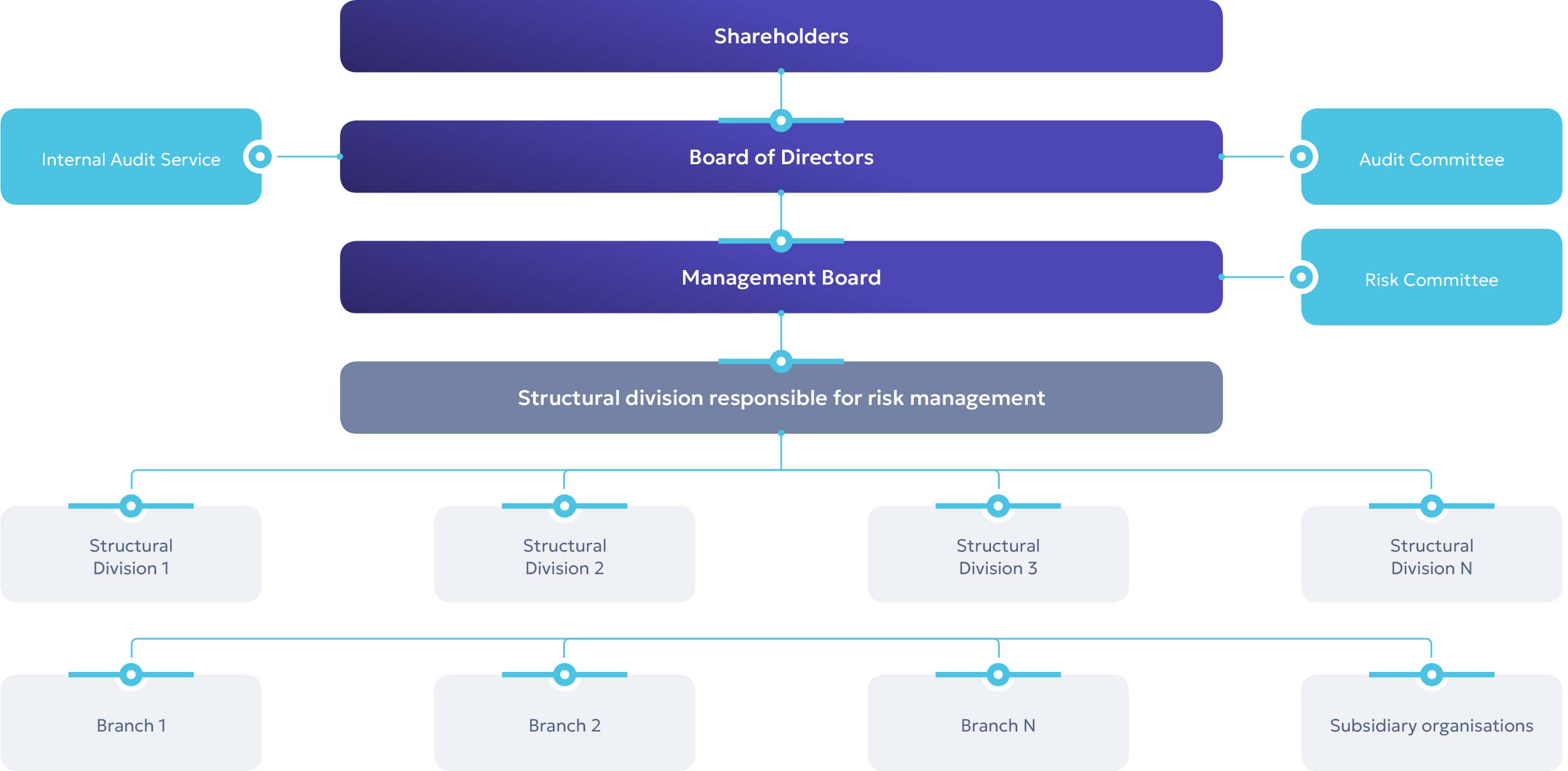
Functions and responsibilities of RMS participants:
- The Board is responsible for the effective operation and development of the RMS as a whole, setting the tone for risk management, and is responsible for implementing mechanisms to ensure that this tone is reflected throughout the Company and the subsidiary organizations and approves key RMS documents;
- The Audit Committee acts in the interests of the shareholder(s) and its work is designed to assist the Board by making recommendations to monitor the robustness and effectiveness of the RMS. Documents submitted for approval by the Board of Directors are preliminarily reviewed by the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
The IAS is responsible for regularly auditing the RMS and providing an independent opinion to the Board of Directors/Audit Committee:
- audits and analyses the effectiveness of risk management procedures and methodology in the area of RMS, and prepares proposals to improve the effectiveness of risk management procedures;
- submits the Report on RMS efficiency to the Board of Directors;
- provides information to the structural Division responsible for risk management on realized risks identified during audits;
- fulfils other functions in accordance with the approved regulatory documents of KEGOC JSC.
The Management Board is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and applying risk identification, assessment and management procedures, organizing the effective functioning of the RMS, supporting structural units in implementing/improving risk management processes in their activities, and ensuring that employees of the structural unit responsible for risk management have professional qualifications.
KEGOC JSC structural divisions, branches and subsidiaries are risk owners and are responsible for risk identification, analysis, risk assessment, risk management, preparation of proposals for mitigation of key risks, reporting on KEGOC JSC key risks and timely informing about the realized risks.
The Compliance Service is responsible for the development and implementation of a compliance programme aimed at managing the risks of violation of the Code of Conduct, anti-corruption legislation and other regulatory requirements applicable to KEGOC JSC.
The Risk Committee, whose task is to make decisions on KEGOC JSC risk management issues and prepare recommendations to KEGOC’s Management Board on the Company’s risk management issues. In 2023, the Committee held 9 meetings.
The structural division responsible for risk management, for development of RMS, clarification of internal and external requirements, provision of consulting assistance, develops IRDs on RMS, monitoring of implementation of risk management measures and preparation of quarterly reporting on risks for the Risk Committee, Management Board and Board of Directors.
In performing their functions, the Board of Directors and the Management Board rely on the ‘Three Lines of Defence’ model, which interacts within the framework of the RMS.
The first line of defence is represented by structural divisions represented by each employee within their competence.
The second line of defence is represented by structural divisions performing monitoring functions.
The third line of defence is represented by the Internal Audit Service, which independently assesses the effectiveness of and contributes to the improvement of risk management and internal control, supports the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors by providing them with an independent assessment of the effectiveness of RMS and internal control.
On a regular basis, KEGOC JSC analyses existing risks and identifies new risks that may adversely affect the achievement of goals, objectives, indicators, and fulfilment of the KEGOC JSC Development Plan (Strategy), Action Plan (Business Plan) of KEGOC JSC.
The following methods are used for risk identification:
- analysing business processes;
- collection and analysis of statistical data;
- individual expert methods (questionnaires, interviews);
- group methods (brainstorming, business game);
- monitoring of publications and speeches.
Risks may also be identified when considering issues submitted to the meetings of the Management Board, Board of Directors, changes in the external environment, changes in KEGOC JSC processes, procedures, organisational structure, etc.
Risks are identified on the basis of existing goals (KPIs) of the Management Board members, management employees, heads of structural divisions of the current year, which are formed on the basis of strategic goals of KEGOC JSC.
In the process of risk inventory, a risk assessment is carried out in parallel with the determination of approaches to risk management.
Within the framework of risk assessment the following risk parameters are assessed:
- the impact (size) of the risk;
- probability of realisation (frequency) of risk;
- impact time.
When assessing risks, qualitative or quantitative analyses or a combination of both are used.
Assessment of risk realisation probability, impact, impact time is carried out in accordance with the risk assessment criteria established in KEGOC JSC. The results of the risk assessment process are plotted on the Risk Map, which visually reflects the relative importance of each risk. Risks are ranked into low, medium, large and critical risks.
Preventive and reactive measures are developed for all identified risks and approved by the Board of Directors. Key risk management measures are aimed at preventing risks and/or minimising the consequences in the event that risks materialise.
All identified risks with their assessment and measures are approved by the Board of Directors.
Classification of KEGOC JSC risks
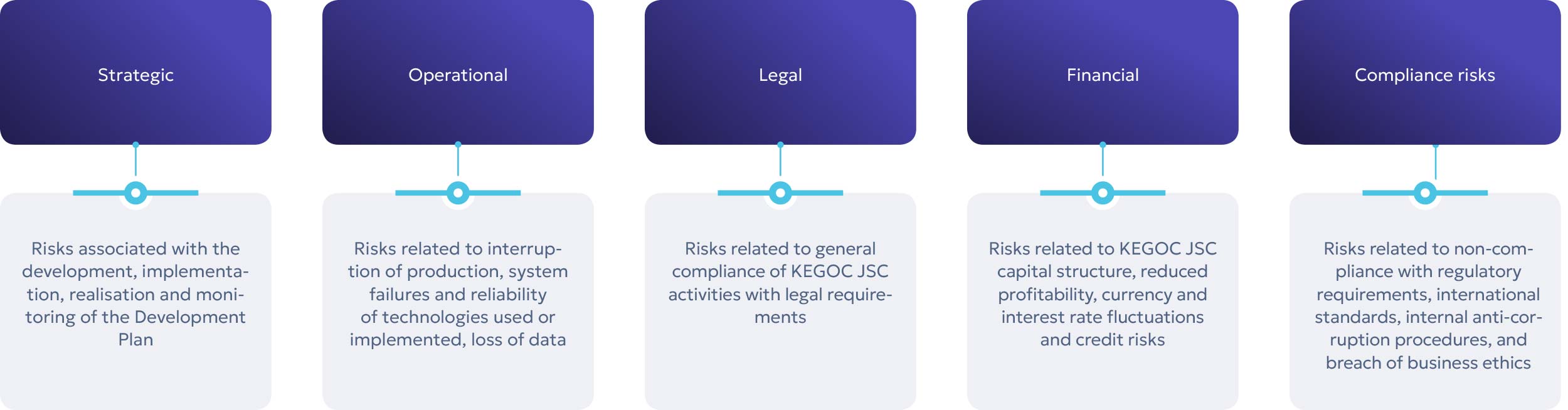
The results of risk identification and assessment are summarized in the Company’s Risk Register for 2023, which includes 50 risks. Measures for their management have been developed for each risk, and risk owners have been identified. The Company continuously monitors the dynamics of key risks and the implementation of mitigation measures by sending quarterly risk reports to the Management Board and the Board of Directors of the Company.
Risk map of KEGOC
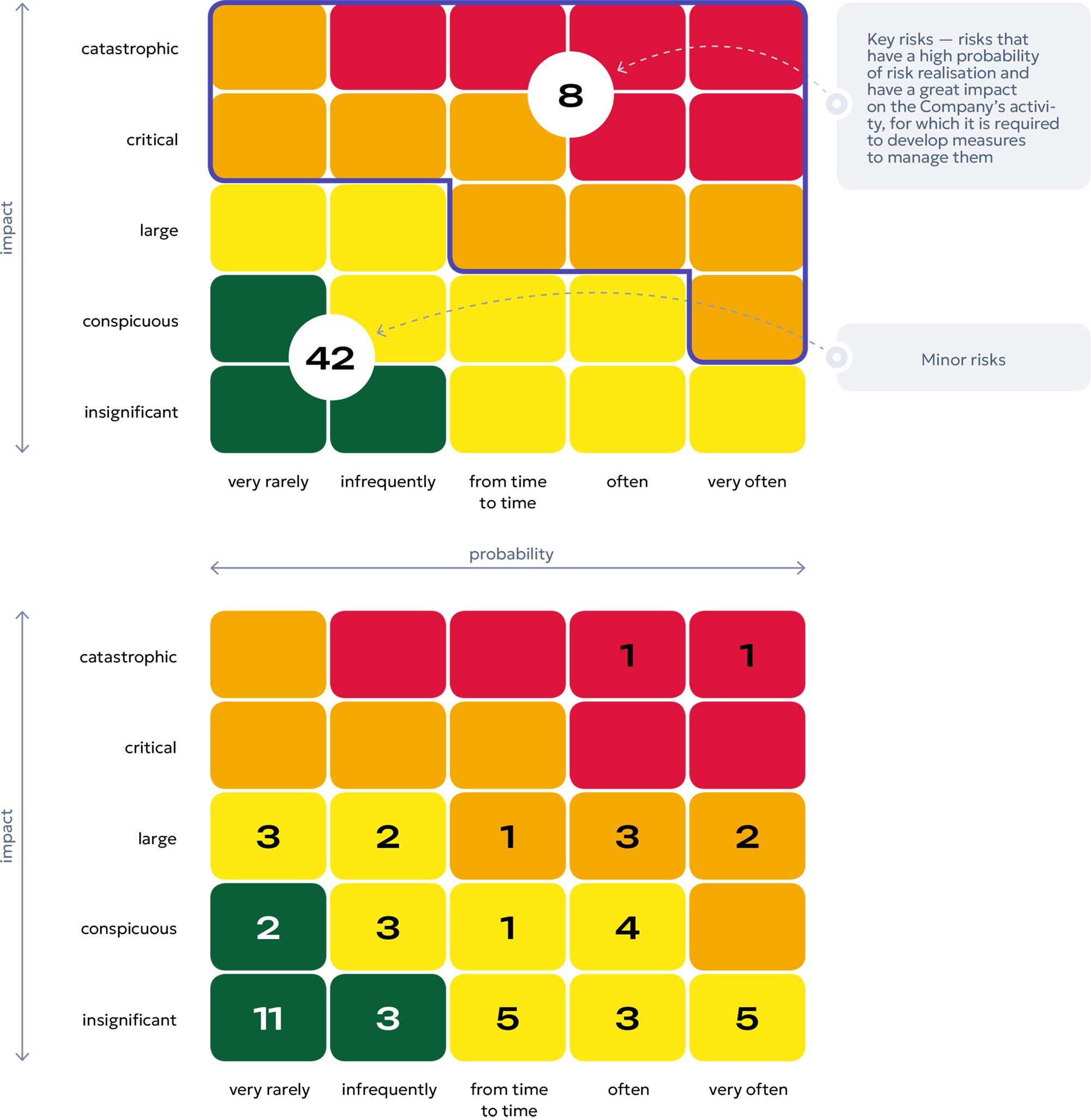
The most important and relevant risks of KEGOC JSC for the reporting year:
- risk of labour-related accidents;
- failure of production assets;
- risk of power shortage in the UPS of Kazakhstan;
- interest rate risk;
- the risk of growth of overdue receivables for system services rendered.
More detailed information on key risk management is disclosed in the relevant sections of this report on the areas of activity and implementation of the Company’s strategic goals.
In addition to the main risks, the Company has considered emerging risks, which are at the stage of identification and/or may significantly increase in the future and may have a significant impact on the Company’s operations. Currently, emerging risks include climate change; global pandemics affecting international trade or global supply disruptions; and geopolitical risks.
KEGOC JSC internal control system (ICS) uses the COSO model and includes five interrelated components: control environment, risk assessment, control procedures, information and communication, and monitoring.
KEGOC JSC Internal Control System Policy defines internal control as a process carried out by the participants of the internal control system in order to achieve the set objectives in three key areas:
- operational activities;
- preparation of financial statements;
- compliance with regulatory and legislative requirements.
The ICS provides for the Company to build a management system capable of responding quickly to process risks, controlling the main and auxiliary business processes and daily operations, and immediately informing the appropriate level of management of any significant deficiencies and areas for improvement.
In accordance with the Regulations on organising and carrying out work on KEGOC JSC internal control system, the competence of the bodies included in the ICS is delineated depending on their role in the processes of development, approval, application and assessment of ICS efficiency. The Board of Directors and the Management Board of the Company in performing their functions rely on the ‘Three Lines of Defence’ model. ICS participants are the Board of Directors, the Management Board, the Audit Committee, the Internal Audit Service, structural subdivisions — owners of business processes and subprocesses, executors of control procedures, structural subdivision responsible for risk management.
The IAS is responsible for the direct assessment of ICS efficiency, testing the operational efficiency of control procedures, and preparing and submitting relevant reports for the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors.
On an annual basis, based on the Company’s register of business processes, the Company approves a plan for assessing the design of control procedures, within the framework of which the effectiveness of the design of control procedures is analysed. Based on the results of this analysis, recommendations for their improvement and areas for improvement are developed.
The Company has implemented a business continuity management system that identifies business processes/sub-processes that require the development of BCM plans. In 2023, work was carried out to identify critical business processes/sub-processes of the Company, for which BCM plans were developed and tested, in particular, for the provision of technical dispatching services of the system operator, for ensuring safety in the field of labour protection and reliability of equipment operation, for provision and support of ICT services, for management of information security incidents and KEGOC JSC activities in case of emergencies.
On an annual basis, the Internal Audit Service of KEGOC JSC assesses the effectiveness of the CRMS and ICS submitted to the Company’s Board of Directors. According to the results of the assessment carried out by the IAS in 2023, the internal control and risk management systems are functioning in an acceptable form providing reasonable assurance of achieving the Company’s objectives. Corrective action plans have been developed for all identified non-compliances based on the recommendations of the IAS, and their implementation is monitored on an ongoing basis.